Search Results for: extracellular fluid
Body fluid
Body Fluids Definition What is body fluid? Literally, body fluid is the fluid of the body. The adult human body is ~50-60%... Read More
Extracellular fluid
Definition noun The body fluid outside the cell composed of blood plasma, interstitial fluid, lymph and transcellular... Read More
Pinocytosis
Pinocytosis Definition What is pinocytosis? Pinocytosis is the ingestion of extracellular fluids, i.e. the fluid... Read More
Fluid mosaic model
Fluid Mosaic Model Definition What is the fluid mosaic model? The fluid mosaic model is a three-dimensional representation... Read More
Cell adhesion
Cell Adhesion Definition Cell adhesion is the process in which a cell uses a specialized complex of proteins to get... Read More
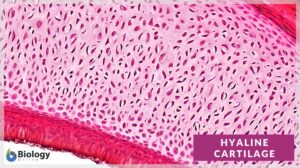
Hyaline cartilage
Hyaline Cartilage Definition Before we define hyaline cartilage, let us understand what cartilage is. What is cartilage? Is... Read More
Transcellular fluid
Definition noun A bodily fluid found in chambers created by the linings of epithelial cells Supplement The extracellular... Read More
Kidneys and Regulation of Water and Inorganic Ions
Renal Functions Kidneys remove/add substances from/to the plasma.Regulate water concentration, inorganic ion... Read More
Saline solution
Saline Solution Definition Saline solution is one the most medically-used solution, which contains sodium chloride... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Hyperosmotic
Hyperosmotic Definition What is hyperosmotic? The word hyperosmotic is derived from two Greek words: 'hyper', meaning... Read More
Movement of Molecules Across Cell Membranes
Diffusion Diffusion is essentially the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower... Read More
Interstitial fluid
Definition noun The fluid found in the intercellular spaces composed of water, amino acids, sugars, fatty acids,... Read More
Neural Control Mechanisms
Nerve cells called neurons generate electric signals that pass from one end of the cell to another and release chemical... Read More
Plasma membrane
Do all cells have a plasma (or cell) membrane? Yes, all cells have a biological membrane that separates the protoplasm from... Read More
Sarcolemma
Sarcolemma Definition What is the sarcolemma? It is the thin, transparent, extensible plasma membrane of the muscle cell.... Read More
Intracellular fluid
Definition noun The body fluid within the cell composed mainly of water dissolved ions, and other molecules Supplement The... Read More
Cell Structure
The interior of human cells is divided into the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is a spherical or oval-shaped... Read More
Extracellular
Definition adjective Occurring or being (situated) outside the cell or cells. Supplement For example, extracellular fluid is... Read More
Turgor pressure
In biology, turgor pressure pertains to the pressure that is exerted by the fluid (e.g. water) against the cell wall. It is... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
Homeostatic Mechanisms and Cellular Communication
Homeostasis is the relatively stable conditions of the internal environment that result from compensatory regulatory... Read More
Hypertonic
Hypertonic Definition Hypertonic is a term used to describe an entity being in the state of hypertonicity, where there is a... Read More
Concentration gradient
What is a concentration gradient? A gradient is a measure of how steep a slope is. Thus, a concentration gradient would be... Read More
Cell membrane
Cell Membrane Definition Just like any non-living body possesses a plastic or paper packaging material that keeps the... Read More
Glycocalyx
What is the Glycocalyx? The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering... Read More
Selectively-permeable membrane
Selectively Permeable Membrane Definition We can define selectively permeable membranes as those that are selectively... Read More
Blood-brain barrier
Definition noun A semipermeable membrane that serves as a selective barrier separating the circulating blood and the... Read More
Energy coupling
What is Energy Coupling? Work, whether it be physical or biological, requires energy to be expended. In biological... Read More
Facilitated diffusion
Facilitated diffusion is the transport of substances across a biological membrane from an area of higher concentration to an... Read More